
This article describes what a low basal body temperature (BBT) is. Also, how to understand if it is normal or one should consult a specialist? The examples of pregnant and non-pregnant graphs with a low BBT in the first and second phases are provided. Is it true that the basal temperature lower than 37 °C (98.60 °F) is bad?.. Is it interesting? Then continue to read.
What does a low basal body temperature in the first and second phase of the cycle means?
If, for example, the basal temperature is lower than 37 °C (98.60 °F) in the second phase of the cycle it doesn’t totally mean that there is a lack of progesterone or a potential problem with a childbearing. It’s not the absolute 37° index but a relative one that matters. What is the difference between the temperatures between the two phases?
![]() Example (!): If the average index before the ovulation is 36.4 °C, and after it is 36.8 °C, the difference is 0.4° (98.24-97.52=0.72 °F). It means that everything is ok with the hormonal background and there are no problems. If the indexes are the following: 36.6 °C and 36.8 °C, the difference is 0.2 °C (98.24-97.88=0.36 °F), which indicates a hormonal disorder. In the second example, one can talk about a low BT in the second phase.
Example (!): If the average index before the ovulation is 36.4 °C, and after it is 36.8 °C, the difference is 0.4° (98.24-97.52=0.72 °F). It means that everything is ok with the hormonal background and there are no problems. If the indexes are the following: 36.6 °C and 36.8 °C, the difference is 0.2 °C (98.24-97.88=0.36 °F), which indicates a hormonal disorder. In the second example, one can talk about a low BT in the second phase.
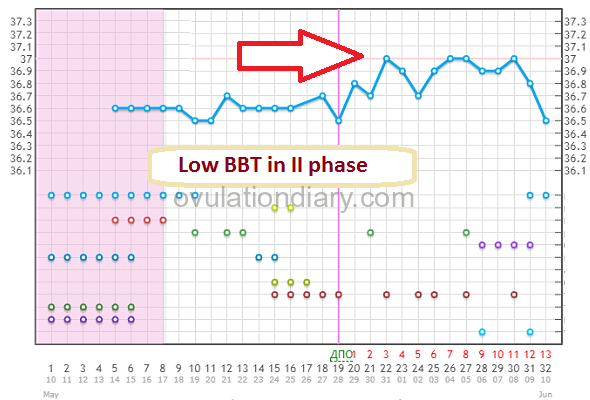
In the first phase a low basal body temperature doesn’t happen. Every woman has her own individual index but not higher than 37 °C (98.60 °F).
The reasons for a low basal body temperature in the second phase
- Lack of progesterone. It is defined by the analysis in the phase of a yellow body (7 days past ovulation);
- Anovulatory cycle. It is defined by the means of folliculometry;
- Wrong BT measurements (change of thermometer, place of measuring, time, sickness in the I phase and etc.);
- Other gynecological and endocrine diseases.
![]() Note (!): The consultation of a specialist and examinations are needed only when in a situation with a low BBT in the II phase that repeats several cycles in a row. Individual, non-repeating chart failures are possible and probably won’t have any threat for potential childbearing.
Note (!): The consultation of a specialist and examinations are needed only when in a situation with a low BBT in the II phase that repeats several cycles in a row. Individual, non-repeating chart failures are possible and probably won’t have any threat for potential childbearing.
Pregnancy graphs with low basal temperature
I’ll repeat now that one can talk about a low BBT only if the graphs have been kept for three or more cycles, the average temperature of the follicular phase is definitely known and the difference between the two phases is 0.25 °C (0.45 °F) and less.
Normal pregnancy is possible with the indexes up to 37 °C (98.60 °F) and a relative difference of 0.3 °C (0.54 °F) and higher. It’s not considered to be a problem but just a peculiarity of the organism.
Below are the graphs of BBT with a successful pregnancy and t° lower than 37 °C:
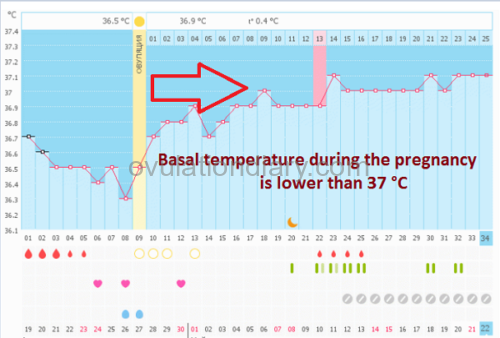
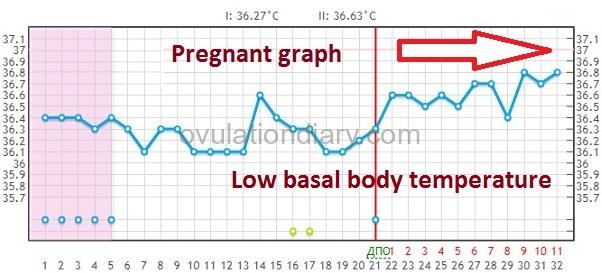
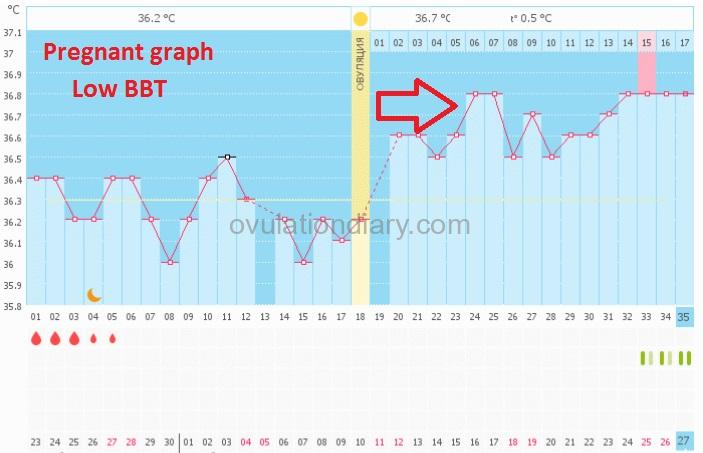
![]() Important (!): A short term decrease of BBT is possible during the confirmed pregnancy. There is no need to panic and start taking medicine containing progesterone. Only a specialist can prescribe them. Watch your state and make the right decision!
Important (!): A short term decrease of BBT is possible during the confirmed pregnancy. There is no need to panic and start taking medicine containing progesterone. Only a specialist can prescribe them. Watch your state and make the right decision!
In this article (on ovulationdiary.com) I explain how to understand a sudden drop of BBT temperature in the first phase before ovulation in different periods after ovulation occurs.
Have a successful planning!
