
Ovulation and conception occur within 24 hours after ovum release. Ovulation occurs approximately 14 days (or 12-16 days) before the next menstruation. If during this period there was unprotected intercourse – pregnancy is possible. First symptoms of successful conception manifesting themselves only after implantation. It is normally within 7-10 days past ovulation (less common – before or after this period). Most common symptoms:
- implantation bleeding;
- BBT drops by 0.2-0.4 °C or 0.36-0.72 °F, for 1 day;
- pulling pain in the lower abdomen or lower back.
Is it possible to conceive on the ovulation day?
During sexual intercourse (SI), up to 250 million spermatozoa enter the female body, but fertilization can occur only if a mature ovum is in their way (in rare cases, a few ovums). Release of the ovum from the follicle is called – ovulation (read more about symptoms and sensations in this material), it is also the shortest stage of the menstrual cycle.
The probability of conception on the ovulation day – is 21.20%. About one in five women become pregnant after SI on the day of ovulation.
This is the highest probability rate in the menstrual cycle. It is due to the fact that a mature ovum does not retain fertility for long. The ovum has a 24 hours lifespan. Sperm live longer – up to three days (in rare cases up to seven days).
So, a woman can become pregnant if intimacy occurs within the period of 3 days before ovulation until the next day after it.
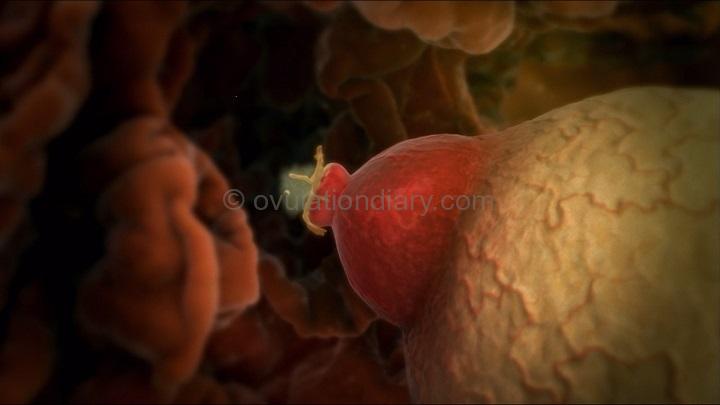
The ovum is most fertile (ready for a zygote formation) precisely at the time of ovulation – immediately after leaving the follicle. During this period, the blood estrogen level reaches its maximum for successful conception.
After the end of ovulation process, the level of sex hormones begins to decline, the ovum’s fertilization ability fades away along with its natural depletion and destruction. If during the fertility window it had no chance to turn into a zygote, it disintegrates in the Fallopian tube and leaves the body with the next menstrual flow.
On what day after ovulation does fertilization occur?
Healthy spermatozoa (sperm) that had entered the female body, usually can remain viable from 2-3 up to 5 days (rarely 7). Therefore, conception after ovulation is possible even if sexual intercourse was several days before the ovum would be released. Moreover, carriers of Y-chromosomes (male gender) are faster and less durable. Their lifespan may be limited to two days. Spermatozoa with X-chromosomes are slower, but active up to 5 days (rarely 7).
![]() Spermatozoa can cover the distance from the vagina to the ampullary region of the Fallopian tube, where the mature ovum is located, in about one and a half to two hours. Therefore, conception may coincide with the day of ovulation. After three days, the ability of sperm to fertilize sharply decreases. About 10.3% of pregnancies occurred after SI one day after ovulation, 0.8% – two days past ovulation.
Spermatozoa can cover the distance from the vagina to the ampullary region of the Fallopian tube, where the mature ovum is located, in about one and a half to two hours. Therefore, conception may coincide with the day of ovulation. After three days, the ability of sperm to fertilize sharply decreases. About 10.3% of pregnancies occurred after SI one day after ovulation, 0.8% – two days past ovulation.
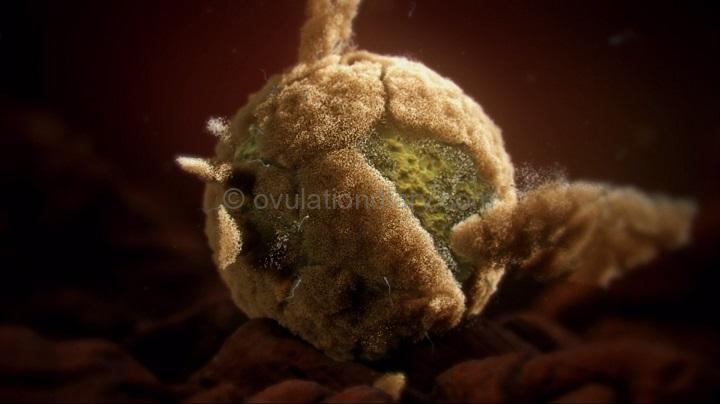
Gynecologists and obstetricians are in no hurry to call the successful merger of male and female germ cells – fertilization. It could be called that only after the zygote had entered the uterus and is implanted in its wall. This process, including conception after ovulation, lasts about 6-7 days.
The first signs of conception after ovulation
After fertilization has occurred (after ovulation), and the zygote has penetrated the wall of the uterus, serious body changes start to happen. It actively prepares for bearing.
![]() Expectant mother could feel the pregnancy literally from the moment of embryo implantation. This moment is often accompanied by tingling and heaviness in the lower abdomen, sometimes with a small amount of yellowish/brownish mucus discharge from the vagina.
Expectant mother could feel the pregnancy literally from the moment of embryo implantation. This moment is often accompanied by tingling and heaviness in the lower abdomen, sometimes with a small amount of yellowish/brownish mucus discharge from the vagina.
A woman can also recognize pregnancy by other symptoms. Some of them:
- Implantation bleeding.
- Implantation BBT dip.
- Nervous tension, resembling PMS symptoms.
- New taste preferences, increased appetite.
- Aversion to certain odors.
- Digestive problems for no apparent reason (nausea, bloating and fullness, upset stomach, morning sickness).
- Frequent urge to urinate (due to an imbalance in the vaginal microflora, as a result of a hormonal background change). Symptoms are different from cystitis – the urine is clear, there is no characteristic pain. Pain may be localized above the pubis.
- Broken attention, fatigue.
- Breast hypersensitivity (tingling, pain, itching, swelling, burning sensation). This is a consequence of a sharp increase in blood hCG level (“pregnancy hormone”) immediately after embryo implantation. Irritation of the nerve endings caused by rapid breast glandular tissue growth.
- Low blood pressure, increasing basal body temperature and subfebrile body temperature. Chills and fever. Higher risk of getting a cold.
- Pulling pain in the lower abdomen or lower back.
Traditionally, the main symptom of conception is lack of menstruation. But other subtle manifestations of pregnancy also should be taken into account, since a menstrual cycle failure can be triggered by medication, stress, acclimatization and other factors.
How to find out if conception has occurred after ovulation?
To determine at the early stages (before menstruation date) whether conception has occurred after ovulation, various methods can be used:
- draw conclusions based on the characteristic symptoms listed above;
- Ultrasound. This procedure will also confirm or rule out the development of an ectopic pregnancy;
- checking the hCG level. A blood or urine test will give an accurate answer one week after conception. Special pregnancy tests (inkjet, cassette, electronic, strip strip) — after 7-10 days, depending on the sample selected;
- presence of uncharacteristic fluctuations in the BBT chart, relative to previous cycles.
Basal body temperature after ovulation if fertilization has occurred
Keeping a basal body temperature chart for at least three menstrual cycles would allow you to detect conception before this fact is confirmed by tests. When pregnancy occurs, the BBT chart would differ from normal cycles.
![]() If fertilization and implantation follow the follicle rupture, the curve on the BBT chart goes sharply down by 0.2-0.3 °C (0.36–0.54 °F) on the 7-10th day (implantation dip is not always obvious on the chart). Then (usually by the next day) it swiftly goes back up and remains stable. BBT stays elevated even during next menstrual cycle onset/delay.
If fertilization and implantation follow the follicle rupture, the curve on the BBT chart goes sharply down by 0.2-0.3 °C (0.36–0.54 °F) on the 7-10th day (implantation dip is not always obvious on the chart). Then (usually by the next day) it swiftly goes back up and remains stable. BBT stays elevated even during next menstrual cycle onset/delay.
There are other salient features of the pregnancy chart, as well as other early symptoms of successful conception. You can read more about them in this article.
